You are taking part in the development of a ``New Generation'' operating
system and the NG file system. In this file system all disk space is divided
into N clusters of the equal sizes, numbered by integers from 1 to
N. Each file occupies one or more clusters in arbitrary areas of the
disk. All clusters that are not occupied by files are considered to be free. A
file can be read from the disk in the fastest way, if all its clusters are
situated in the successive disk clusters in the natural order.
Rotation of the disk with constant speed implies that various amounts of
time are needed for accessing its clusters. Therefore, reading of clusters
located near the beginning of the disk performs faster than reading of the ones
located near its ending. Thus, all files are numbered beforehand by integers
from 1 to K in the order of descending frequency of access. Under the
optimal placing of the files on the disk the file number 1 will occupy clusters 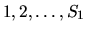 , the file number 2 will
occupy clusters
, the file number 2 will
occupy clusters 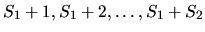 and so on (here
Si is the number of clusters which the i-th file
occupies).
and so on (here
Si is the number of clusters which the i-th file
occupies).
In order to place the files on the disk in the optimal way cluster-moving
operations are executed. One cluster-moving operation includes reading of one
occupied cluster from the disk to the memory and writing its contents to some
free cluster. After that the first of them is declared free, and the second one
is declared occupied.
Your goal is to place the files on the disk in the optimal way by
executing the minimal possible number of cluster-moving operations.
The first line of
the input file contains two integers N and K separated by a space
( 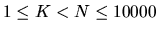 ). Then K lines follow, each of them describes one file. The
description of the i-th file starts with the integer
Si that represents the number of clusters in the
i-th file (
). Then K lines follow, each of them describes one file. The
description of the i-th file starts with the integer
Si that represents the number of clusters in the
i-th file ( 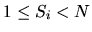 ).
Then Si integers follow separated by spaces, which
indicate the cluster numbers of this file on the disk in the natural order.
).
Then Si integers follow separated by spaces, which
indicate the cluster numbers of this file on the disk in the natural order.
All cluster numbers in the input file are different and there is always
at least one free cluster on the disk.
Your program
should write to the output file any sequence of cluster-moving operations that
are needed in order to place the files on the disk in the optimal way. Two
integers Pj and Qj separated
by a single space should represent each cluster-moving operation.
Pj gives the cluster number that the data should be
moved FROM and Qj gives the cluster number that this
data should be moved TO.
The number of cluster-moving operations executed should be as small as
possible. If the files on the disk are already placed in the optimal way the
output should contain only the string ``No optimization needed".
20 3
4 2 3 11 12
1 7
3 18 5 10
2 1
3 2
11 3
12 4
18 6
10 8
5 20
7 5
20 7
Miguel Revilla
2000-05-22